- Abstract
This document delves into the transformative intersection of Large Language Models (LLMs) and AI agents, two pivotal advancements in artificial intelligence. While LLMs excel in understanding and generating human-like text, they lack the ability to take autonomous actions. In contrast, AI agents are designed for action, capable of decision-making and execution. This exploration highlights how the integration of these technologies can bridge the gap between comprehension and action, unlocking new possibilities for businesses across various industries.
1.1 Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is evolving at a rapid pace, with two of its most prominent advancements being Large Language Models (LLMs) and AI agents. While LLMs like GPT-4 have revolutionized natural language processing through unparalleled comprehension and contextualization, they fall short when it comes to taking autonomous actions. AI agents, on the other hand, are action-oriented systems capable of decision-making and execution. This document explores how combining these two technologies bridges the gap between understanding and action, creating transformative possibilities for businesses.
1.2 End Users
Data professionals such as data scientists, data engineers, data architects, data executives, and organizations from heath care, telecommunication, banking and finance, retail, etc. are the end users who would benefit from this asset.
- What Are Large Language Models?
Large Language Models (LLMs) are AI systems trained on vast datasets comprising text from books, articles, websites, and more. They leverage deep learning techniques, such as transformer architectures, to predict and generate coherent text based on input prompts. Their applications include:
- Text summarization
- Content generation
- Language translation
- Sentiment analysis
2.1 Key Capabilities: Comprehension and Contextualization
- Comprehension: LLMs can parse complex language inputs, understanding nuances like tone, intent, and ambiguity. For instance, they can differentiate between a sarcastic statement and a factual one.
- Contextualization: LLMs excel at maintaining context across long conversations or text, making them invaluable for creating personalized user experiences. For example, in a chatbot, they can refer to earlier parts of the conversation to provide consistent responses.
Limitations: Passive Understanding Without Action
While LLMs are powerful, their capabilities are constrained by their passive nature. They can:
- Generate a list of steps to solve a problem but cannot execute those steps.
- Suggest actions to optimize workflows but cannot initiate changes.
- Understand conversational context but cannot autonomously engage with external systems like APIs or databases. This limitation necessitates the integration of AI agents to enable action.

- AI Agents: Beyond Understanding
AI agents are autonomous systems designed to perform tasks based on goals or instructions. Unlike LLMs, which focus on understanding and generating responses, AI agents prioritize:
- Decision-making
- Task execution
- Learning from outcomes AI agents are proactive, taking steps to achieve objectives with minimal human intervention.
3.1 How AI Agents Leverage LLMs
AI agents rely on LLMs for natural language understanding (NLU) while adding layers of functionality to execute tasks. Key roles include:
- Decision-Making: By analyzing LLM-generated insights, agents choose optimal actions.
- Autonomy: AI agents act independently, accessing databases, APIs, and systems to perform tasks.
- Feedback Loops: Agents can evaluate the success of their actions, refine strategies, and adapt to new conditions dynamically.
3.2 Key Features: Autonomy, Decision-Making, and Execution
- Autonomy: AI agents reduce the need for human oversight by taking proactive measures based on defined goals.
- Decision-Making: These systems analyze data, evaluate options, and choose the best course of action in real time.
- Execution: AI agents can complete tasks end-to-end, such as booking appointments, updating records, or managing IoT devices.

- Combining LLMs & AI Agents for Intelligent Solutions
The integration of LLMs with AI agents results in systems that are both intelligent and actionable. For example:
- An AI-powered customer service bot can not only understand and respond to customer queries but also resolve issues by interacting with backend systems.
- A business assistant can draft an email using an LLM and send it autonomously based on user approval.
4.1 Real-World Scenarios Where Understanding Meets Action
- Customer Support:
- LLMs understand customer complaints in detail.
- AI agents process refunds, update order statuses, or escalate critical issues automatically.
- Data Analysis:
- LLMs extract insights from large datasets.
- AI agents compile actionable reports and distribute them to stakeholders.
- Healthcare:
- LLMs analyze patient records for potential diagnoses.
- AI agents schedule follow-ups or notify physicians about critical findings.
4.2 Overcoming Challenges: Training, Integration, and Scalability
- Training: Ensuring LLMs are fine-tuned for specific industry contexts to improve accuracy and relevance.
- Integration: Embedding AI agents into workflows, ensuring seamless interaction with existing tools and databases.
- Scalability: Building systems capable of handling large-scale operations without performance degradation.

- Applications Across Industries
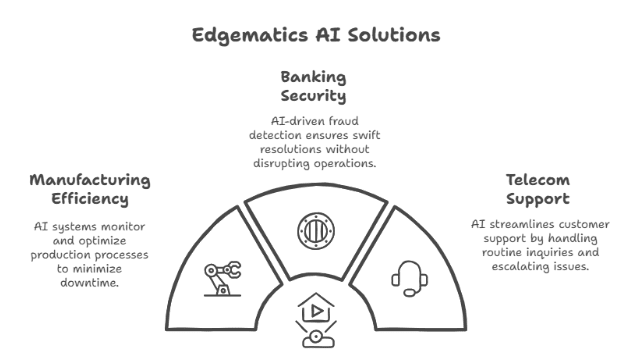
5.1 Banking: Fraud Detection to Automated Resolutions
- LLM Role: Detect unusual transactions through advanced anomaly detection algorithms.
- Agent Role: Automatically flag accounts, notify customers, or initiate investigative workflows to address fraud.
5.2 Manufacturing: Intelligent Process Automation
- LLM Role: Analyze operational data, identifying inefficiencies or potential bottlenecks.
- Agent Role: Modify production schedules, recalibrate machinery, or reorder inventory autonomously.
5.3 Telecom: Enhancing Customer Support and Network Management
- LLM Role: Provide instant, context-aware responses to customer queries.
- Agent Role: Resolve issues like network downtime by autonomously dispatching technical teams or rerouting services.

- Emerging Trends in AI Collaboration with LLMs
- Dynamic Systems: AI agents are evolving to learn new tasks dynamically through LLM integration, enabling continuous adaptability.
- Personalization: Systems are becoming increasingly user-centric, delivering highly tailored experiences by leveraging individual preferences and past interactions.
Ethical and Operational Considerations
- Transparency: Ensuring users understand the decision-making processes behind AI systems.
- Safeguards: Preventing misuse through robust governance and ethical AI frameworks.
- Bias Mitigation: Addressing inherent biases in training data to improve fairness and inclusivity.
- How Edgematics Fuels the Next Phase of AI Advancement
At Edgematics, we are leading the charge in AI innovation by merging the robust language understanding capabilities of large language models (LLMs) with the autonomy and decision-making prowess of AI agents. This powerful combination allows us to provide state-of-the-art solutions that transcend mere passive insights, enabling businesses to engage in proactive and intelligent actions. Below, we outline how we assist organizations in achieving transformative results:
7.1 Automating Complex Workflows
In the current fast-paced business landscape, manual processes can impede growth and efficiency. Edgematics harnesses the combined strengths of LLMs and AI agents to automate complex workflows. For example, our solutions can:
7.2 Driving Efficiency Across Operations
Efficiency is fundamental to sustainable growth, and Edgematics aids organizations in optimizing their operations through AI-powered solutions that identify and eliminate bottlenecks.
7.3 Enhancing Decision-Making with Advanced AI Integrations
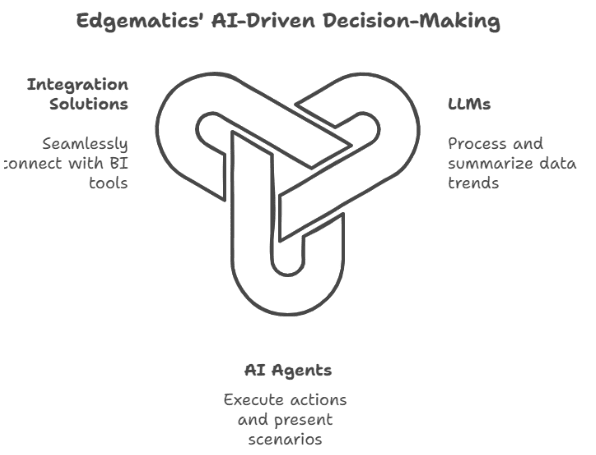
Effective decision-making relies on timely access to actionable insights. Edgematics offers AI integrations that convert raw data into valuable recommendations, enabling organizations to make informed decisions more rapidly. Here’s how we accomplish this:
At Edgematics, we don’t just implement GenAI/LLM solutions, we create intelligent systems that adapt, learn, and grow alongside your business. By combining the cognitive power of LLMs with the operational capabilities of GenAI agents, we empower organizations to unlock new levels of productivity, innovation, and strategic advantage.
Book a Discovery Call with us and find out more.











