Why Every Data Engineer Needs to Understand Edge Computing
As we all are using multiple devices, data is growing exponentially which has created new problems as well as new opportunities. One of the solutions to this problem is edge computing. And data engineers should leverage its potential.
What exactly edge computing is?
Edge computing is a network strategy where data is processed and stored at the edge of the network as close as possible to where the data is generated, rather than relying on centralized data centers or cloud environments.
Now that we’ve mentioned cloud computing, let’s explore the key differences between cloud and edge computing
- Location of Data Processing
- Cloud Computing: Data is processed in centralized data centres which is located far away from the data source.
- Edge Computing: Data is processed at the edge of the network, near to the source of data generation, such as IoT devices or sensors.
When we watch any videos in our phone, it may lag for few seconds or milliseconds as this data is processed far away central servers from the device. but when we talk about a self-driving car it should make decisions immediately without any delay so here comes the edge computing. if we have an edge server in the self-driving car it will make real time decisions on the data which is generated using the sensors
Now, before we know why Every Data Engineer Needs to Understand Edge Computing
Let’s understand why edge computing gained popularity:
Because of its power of minimal latency. Latency is described as the time that elapses between a client initiating contact or making a query and time it takes to receive a response from the computational sources. In cloud computing since the computation is happening far away from source like thousands of miles away there could be a lag in response. This could be a bad user experience.
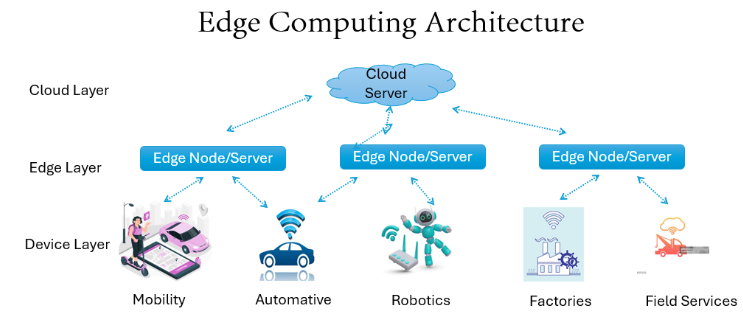
Now let’s deep dive into some advantages of edge computing and that is why every data engineer needs to understand edge computing:
Advantages
1)Reduced Network congestion:
- As the data is processed locally edge computing can help to minimize the amount of data that needs to be transmitted to cloud this can lighten network congestion and reduce latency which is critical in applications that require real time data processing such as industrial automation and robotics.
2)Quick decision making:
- It is possible because the communication time is very minimal, so it simplifies real time decision making that helps in solving security threats. For example, it is quicker to raise trigger alarms since the data flow is smoother.
- This is important for applications like autonomous vehicles, IoT devices, and industrial automation, where rapid responses is the key.
3)Cost effective:
- Since the data bandwidth is low, transmission costs are lower, making edge computing a cost-effective technology.
4)Security:
- As most of the data is processed at the source and is not transferred to a cloud location, there could virtually be no data leaks it is easy to apply traditional encryption and access security protection between edge and cloud servers which makes it less vulnerable and more resilient to surface attacks.
- This is especially important for industries like healthcare and finance, where data privacy is paramount.
5)Enhanced Scalability:
- Edge computing can scale more efficiently than traditional cloud-based solutions by distributing processing power across multiple edge devices.
- This can help organizations handle increasing data volumes and complex workloads.
As we just went through some advantages of edge computing but also, we know “Every coin has two sides” so let’s see some disadvantages of edge computing.
Essential elements for data engineers:
- Data Pipelines
Most data pipelines have only one purpose — to ingest, transform, and load information into structured data warehouses or lakes. Edge computing changes this by enabling localized data storage logic that breaks the flow. This makes them rethink their pipelines in order to merge:
- Pre-processing at the edge.
- Filtering unwanted data before it reaches the cloud.
- Managing Distributed Systems
Edge computing makes data engineers work with a system that is very distributed, so this is what needs to be done:
- Structures that collect and process data from thousands of edge devices which are physically far away should be created,
- Devices at geographically distant sites of the edge level and the core one should synchronize data for spinning together up with coherent logic,
- Manage and Have access to new technologies and tools that can enable control other edge devices in the network.
- Optimizing for Latency and Bandwidth
Applications in gaming, healthcare, or self-driving cars cannot afford latency caused by sending data to remote servers. Data engineers need to:
- Build systems optimized for low-latency processing at the edge.
- Reduce bandwidth costs by preprocessing or aggregating data locally.
- Data Privacy and Compliance
Edge computing keeps sensitive data closer to its source, reducing exposure to security risks during transmission. Data engineers play a key role in:
- Ensuring data encryption and compliance with privacy regulations (like GDPR).
- Designing architectures that anonymize data before forwarding it to central locations.
- Real-Time Analytics
Edge computing enables real-time analytics. Data engineers need to:
- Understand frameworks like Apache Kafka, Flink, or Kubernetes that support real-time edge processing.
- Integrate edge AI models to deliver insights without relying on centralized resources.
Opportunities for Data Engineers
Edge computing offers immense opportunities
- Creating hybrid architectures that combine the best of edge and cloud.
- Enhancing career prospects by mastering a cutting-edge skill set.
- Enabling innovation in industries that rely on real-time decision-making.
How Edge Computing Works
Edge computing involves processing data closer to its source, rather than sending it to a centralized cloud data centre. This is achieved by deploying computing resources, such as servers and storage, at the edge of the network.
Key Tools and Technologies for Edge Computing
- Edge Devices and Gateways:
- Raspberry Pi, NVIDIA Jetson, Intel NUC
- IoT gateways from companies like Advantech, Siemens, and Cisco
- Edge Computing Platforms:
- AWS IoT Greengrass
- Microsoft Azure IoT Edge
- Google Cloud IoT Edge
- Dell Edge Computing Solutions
- HPE Edgeline
- Cloud-Native Technologies:
- Kubernetes
- Docker
- Serverless Functions (e.g., AWS Lambda, Azure Functions)
Examples of Edge Computing Applications
- Autonomous Vehicles: Real-time processing of sensor data for autonomous driving decisions.
- Smart Cities: Analyzing traffic data to optimize traffic flow and reduce congestion.
- Industrial IoT: Monitoring and controlling industrial equipment in real-time.
- Retail: Analyzing customer behaviour and inventory data to improve store operations.
- Healthcare: Processing medical data at the point of care for faster diagnosis and treatment.
By leveraging edge computing, organizations can achieve lower latency, improved reliability, enhanced security, and reduced costs.
Summary
As the data landscape evolves, edge computing is no longer a niche concept—it’s a necessity for modern data engineering. By understanding and leveraging edge computing, data engineers can build resilient, scalable, and efficient systems that unlock the true potential of real-time data.
The future of data engineering lies at the edge. Are you ready to embrace it?
Edgematics – Turning your data into business value.
Author:
Pooja B, Lead Data Engineer at Edgematics











